My main point is that Internet technology today does not support the right of assembly, and therefore it cannot and does not support democracy. The reason is that even though we can easily form groups on Google, Facebook, you name it, we don’t know who the people on the group are.
Archive (Page 6 of 7)
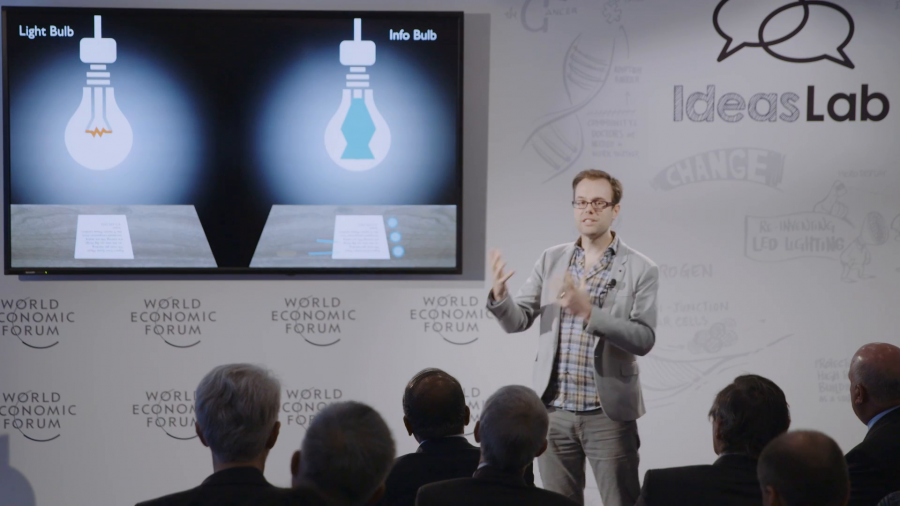

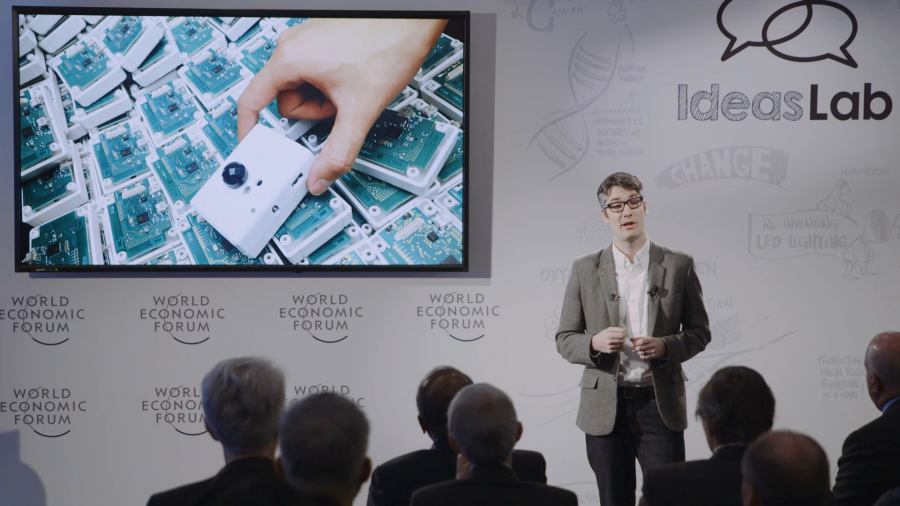
What we’re trying to think about now is, take the sort of venerable light bulb and recast it as a computational appliance. So, how do we take something that’s been so remarkably successful and infuse it with computational abilities?

How can we extend what we are learning about how simple local interactions in ant colonies or in brains, in the aggregate, produce the collective behavior of the group and the way that it responds to changing conditions? How can we extend what we’re learning about collective behavior in other systems to begin thinking about collective behavior in human social organizations?
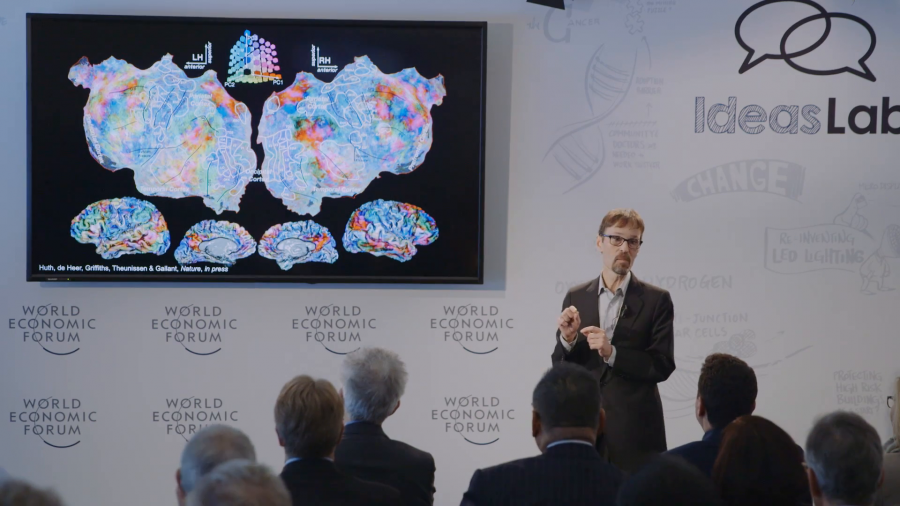
In brain decoding, we take our model that we’ve developed of the brain (and this can be a model for anything, vision or language) and we reverse it. And instead of going from the stimulus to the brain activity, we go from the brain activity back to the stimulus.

Instead of having our children become consumers of robotics technology, consumers of products, we’d have to train them to be producers, to realize that they can use robotic technologies to build something with their intuition, their creativity, and their sense of purpose, that has meaning to them. Then we’d have a technologically fluent society.
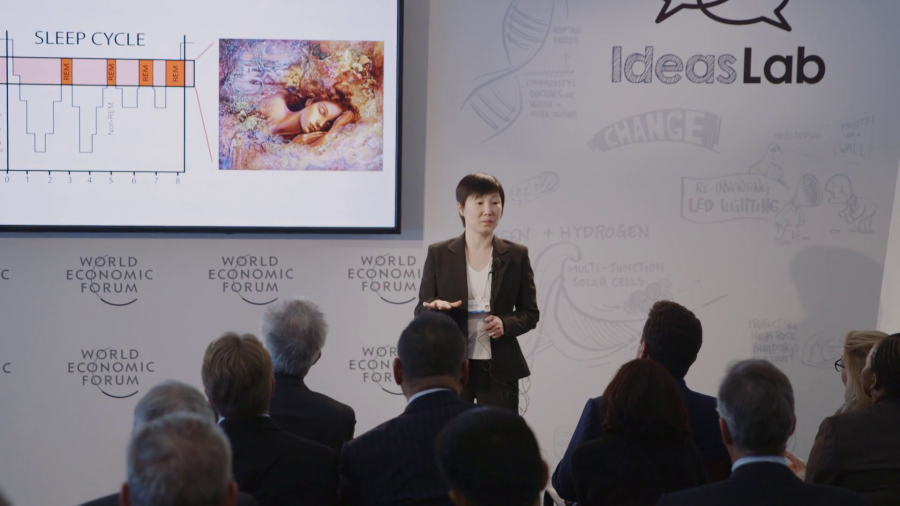

We used to think that sleep is a passive process caused by reduced sensory stimulation so that our normal mental and physical activities can shut down. We held this belief since the time of Aristotle, and perhaps even before that. But now we know that this idea is completely wrong.

We’ve been building autonomous vehicles for about twenty-five years, and now that the technology has become adopted much more broadly and is on the brink of being deployed, our earnest faculty who’ve been looking at it are now really interested in questions like, a car suddenly realizes an emergency, an animal has just jumped out at it. There’s going to be a crash in one second from now. Human nervous system can’t deal with that fast enough. What should the car do?
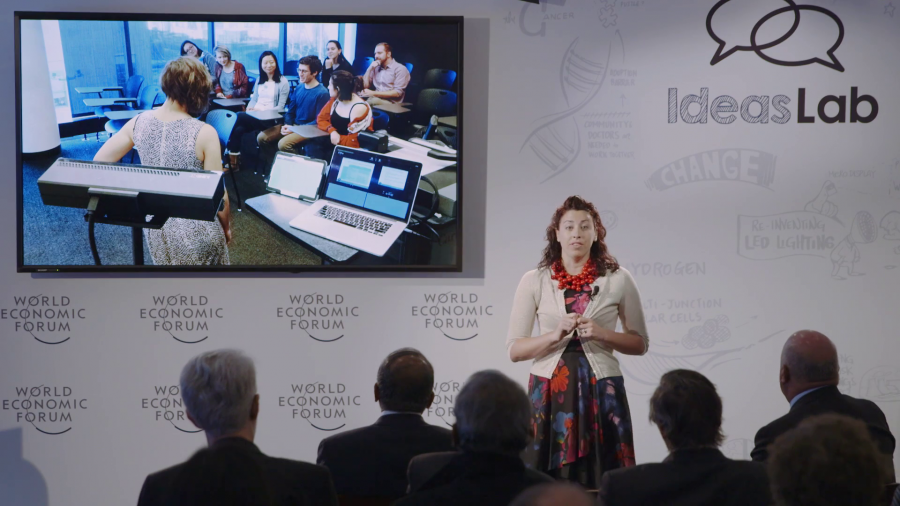

Education has remained largely unchanged for millennia. In any classroom, you see a set of students gathered around a teacher who’s writing on the board, or maybe now we’ve added a PowerPoint deck. But, as in many other fields that have been slow to change, the data revolution is coming for education.

The idea of putting a robot simulator inside a robot, well, it’s not a new idea but it’s tricky and very few people have pulled it off. In fact, it takes a bit of getting your head round. The robot needs to have, inside itself, a simulation of itself and its environment, and others in its environment. And running in real-time as well.


