If you were to ask me what the crisis in the present is, as an evolutionary biologist I have to go back millions of years and try to connect all the dots, going back to man as a single-celled organism to present time, and saying what is it that is causing modern consternation? More importantly, is there a pattern? Has this happened before? Were there some ordinary people like you and I, shopkeepers in Rome, who were standing around and saying, “You know, our leaders don’t seem to be on top of our problems. They seem to be getting worse one generation after another.”
Archive

I don’t think that anything will save the world in the sense of bringing Utopia to Earth. But I think the world could be improved, and that would be the version of the question that I’m very much interested in.

Much of economics and public policy rests on the assumption that increasing the wealth of individuals and nations provides a route to increasing their wellbeing. So why does money fail us?
One of the big things that we’re going to talk about here is paraphilia. We’re going to talk about sexual deviance. We’re going to talk about the problem of people whose sexual desires lead to attraction to children, lead to attraction towards violent sex, lead to sexual transgression in one fashion or another.

When I asked my peers and my professors if they’d ever heard of this type of work, two things happened. The first thing is that they said no, they hadn’t. The second thing they said, which is probably what you’re thinking, is, “Well, can’t computers do that?” And in fact the answer to that is no.

The reason that I am interested in behavioral contagions is that I firmly believe that if we can understand how behaviors spread in a social network and thus in a population from person to person to person to person, that we could potentially promote behaviors like…condom use, or tolerance.

One of the most recent paradigms that we’ve used to try to get this under experimental control is to ask people to act out pretend harmful actions. So for instance, we’ll give them a disabled handgun. We’ll show them that it’s fake. That it couldn’t possibly harm a fly. We put it in their hands and then we ask them to shoot us in the head.

The French philosopher Immanuel Levinas has taught us that it is through our interactions with the face of somebody else, it is through encountering the face of another, that our responsibilities to someone else arise. You cannot look at somebody else, truly look at them, and then walk away without having some kind of sense of a relationship towards that person. But what if the other has no face? What then? Or what if the face of the other is actually the face of another person entirely?
What’s key…is that we all need to work together. There’s no way for all of us to know about each other. We’re in that part of this new way of being that there’s too many players. It’s too chaotic. There is no center, there is no hub. But we need to find ways to work together, and to lose the idea that any one of us is the solution. Because if any one of us were the solution, we wouldn’t be where we are now.
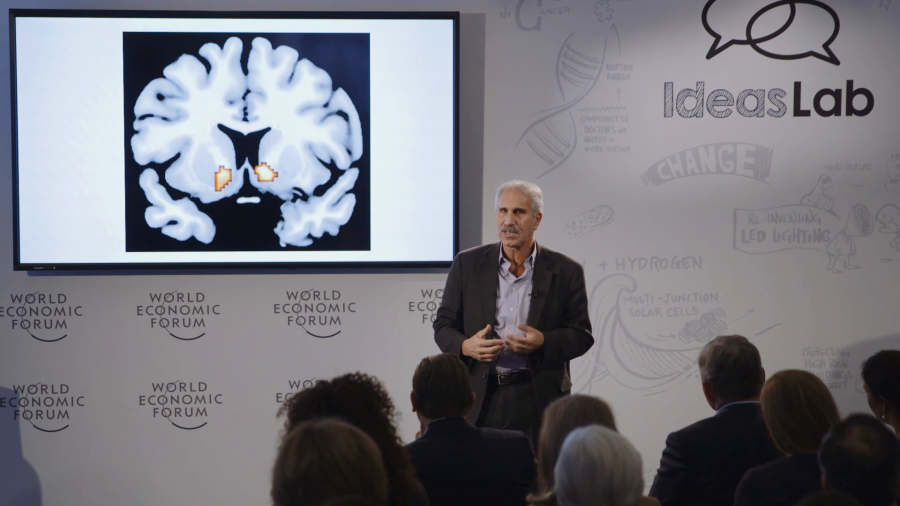
Why do we do the things that we do? Why do we sometimes choose to be loving parents and other times engage in irrational self-destructive behaviors? What drives us to sometimes be altruistic and other times make decisions that really threaten our very survival? Well, the answer lies in our brains. Our brains evolved to ensure that we repeat behaviors that will lead to our survival.
