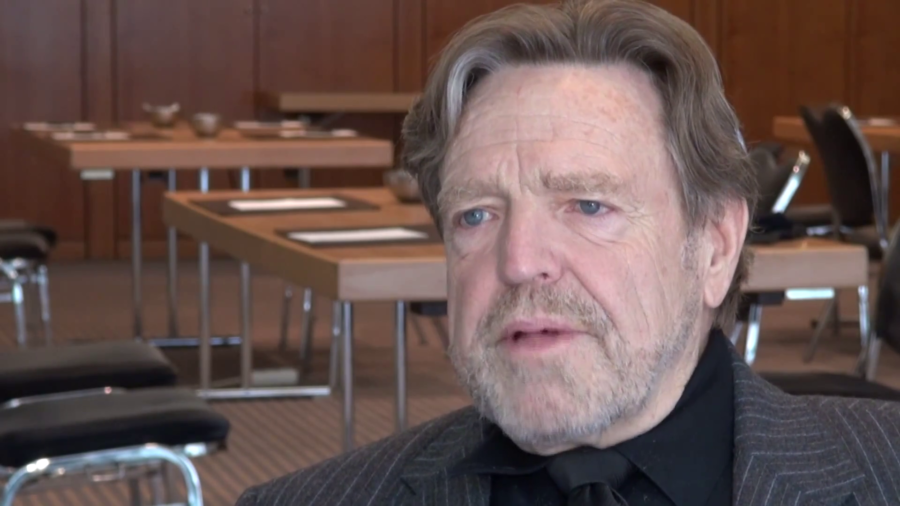
My greatest hope, and the thing I’ve been working for most of my life now, is that it will realize itself as being something that makes it possible for anybody to know anything that they’re capable of knowing. Which I think is a wonderful thought. Or that it will make it possible for anybody that has something important that other people should hear to say it, without any fear of being shut up or coerced or that sort of thing.
Archive
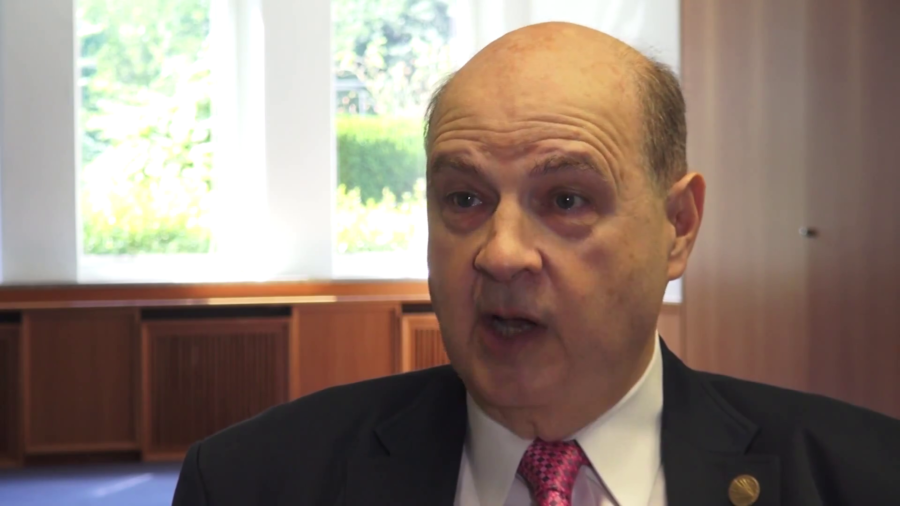

There was really no real security built, other than things like passwords and maybe some encryption here or there. And the attitude that my boss had at National Science Foundation was, “That’s not our concern. This is for the academics. People want to build in all kinds of security, that’s somebody else’s problem.” I think that was a very valid point at that time, but that was 1990.
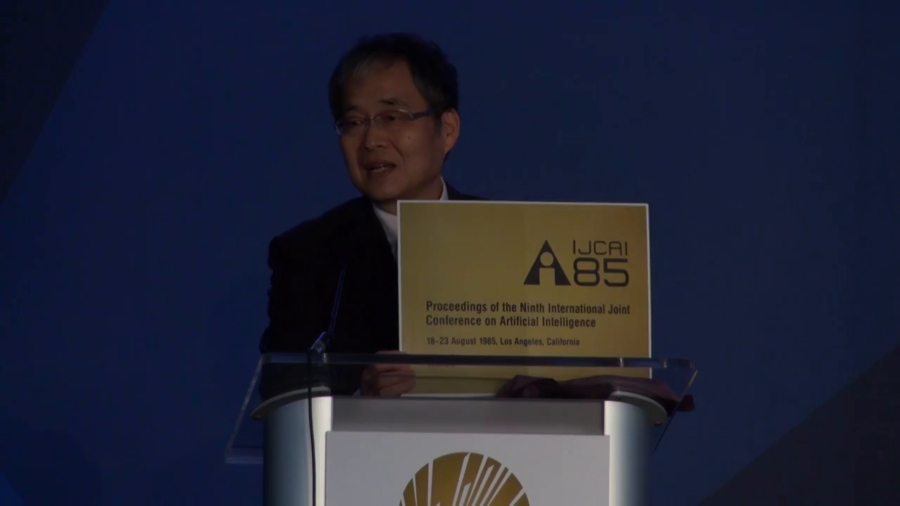

I learned a lesson. It’s acceptable to give up one dream. Still, there should be something for us to contribute to human society. In my life, that was the Internet.
Looking at Brazil again thirty years later, we see the very same situation. And the question is what to do. The whole country has been waiting to see when and how recovery will begin, political, economic and so on.
The interesting phenomenon related to the RSA algorithm and is not shared with some of the other algorithms is it is useful for both encryption and for digital signature. That is they are two distinct uses and this single algorithm is useful for both of those. And there’s an amazing and somewhat interesting story that then develops from that.
The people that invented Ethernet did a real good thing. Ethernet is good technology. But they did a really bad thing because they called it a net. And they shouldn’t have called it Ethernet, they should’ve called it “Etherlink.”
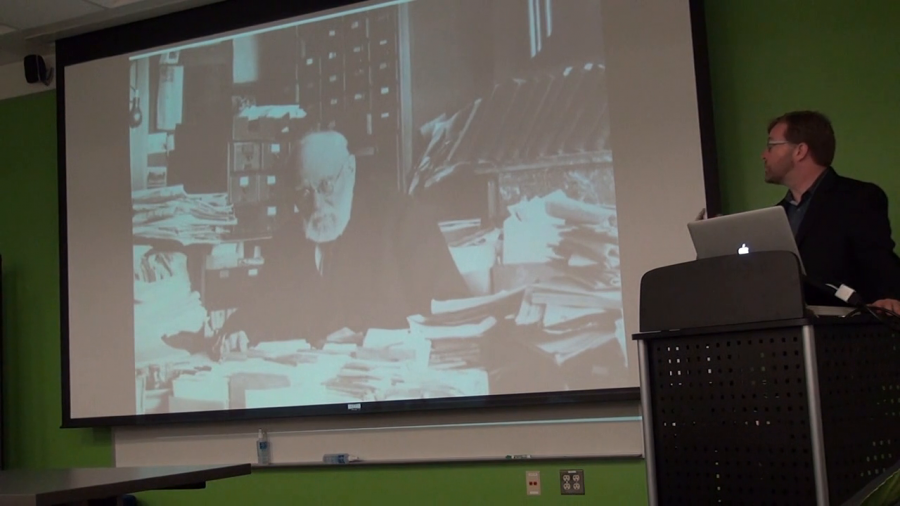

I wanted to give you a little bit of perspective on Otlet’s broader vision, which I think is in a way even more interesting as a reference point for thinking about some of the changes we’re seeing today as our lives are increasingly reshaped by technology and networks. What Otlet offers is a different way into that space, and a different way of thinking about what a networked world could look like.

What I’d like to do for probably the next 40 to 45 minutes is just first of all talk about how Reading Writing Interfaces as well as the Media Archaeology Lab underlie my next/current project that I’m calling “Other Networks,” which will lead me into an explanation of my kind of mysterious title “There Is No Internet.” And I’ll finish with talking about specific examples of other networks. When I say “other networks” I’m talking primarily about networks that were outside or before what we now call The Internet.



