Solar geoengineering rests on a simple idea that it is technically possible to make the Earth a little more reflective so that it absorbs a little less sunlight, which would partly counteract some of the risks that come from accumulating carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. When I say technically possible, it appears that at least doing this in a crude way is actually easy, in the sense that it could be done with commercial off-the-shelf technologies now, and it could be done at a cost that is really trivial, sort of a part in a thousand or a part in ten thousand of global GDP.
Archive
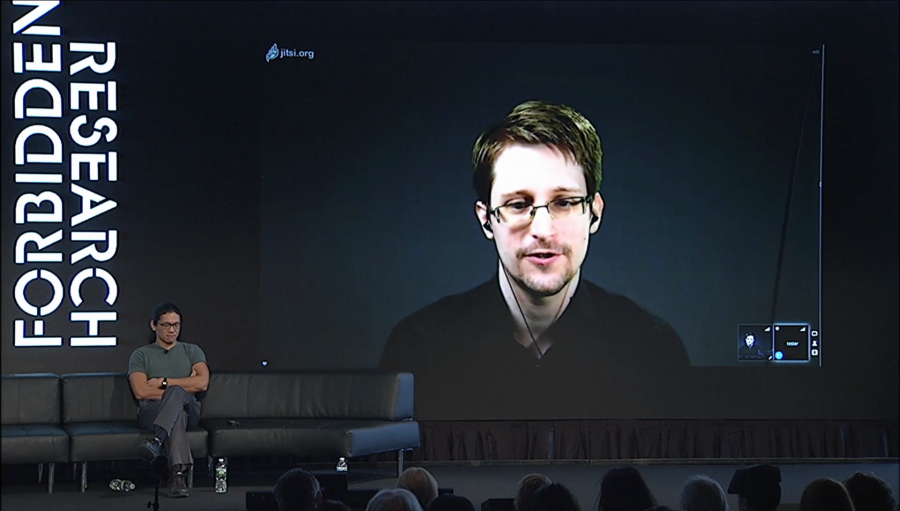
When I announced the talk on Twitter, somebody immediately was like, “Lawful abuse, isn’t that a contradiction?” But if you think about it for just a moment it might seem to be a little bit more clear. After all, the legality of a thing is quite distinct from the morality of it.

As we dug into this topic, we realized research gets forbidden for all sorts of reasons. We’re going to talk about topics today that are forbidden in some sense because they’re so big, they’re so consequential, that it’s extremely difficult for anyone to think about who should actually have the right to make this decision. We’re going to talk about some topics that end up being off the table, that end up being forbidden, because they’re kind of icky. They’re really uncomfortable. And frankly, if you make it through this day without something making you uncomfortable, we did something wrong in planning this event.
Talking to people who study the history of science, and you look at Nobel Prize winners, many of them have really taken sort of career-threatening risks in order to win Nobel Prizes. So even science, which feels like an area where you’re supposed to question authority and think for yourself, you actually have to be rather risk-taking and disobedient.


