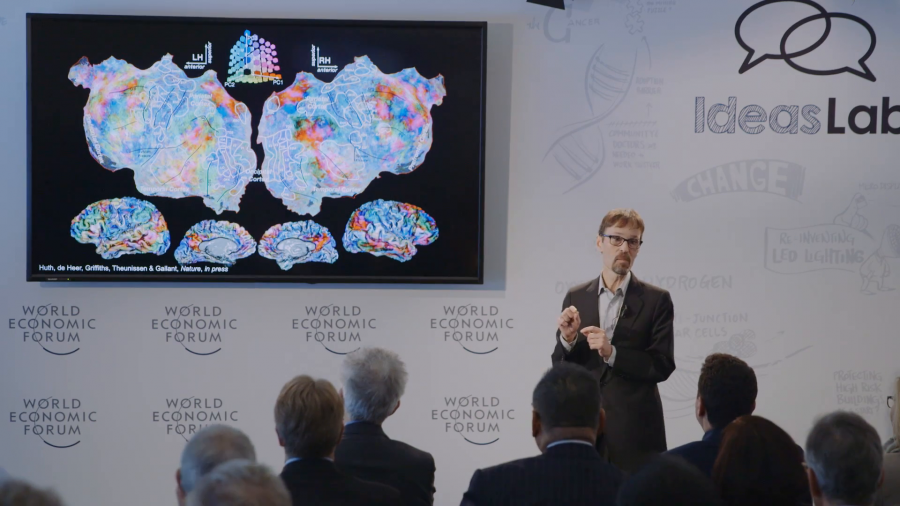
The goal of MICrONS is threefold. One is they asked us to go and measure the activity in a living brain while an animal actually learns to do something, and watch how that activity changes. Two, to take that brain out and map exhaustively the “wiring diagram” of every neuron connecting to every other neuron in that animal’s brain in the particular region. And then third, to use those two pieces of information to build better machine learning. So let it never be said that IARPA is unambitious.
Archive

The thing that makes us unique is our complexity. But not complexity in some generic sense. Nature is rife with complexity. What makes us special is the complexity of our brains.
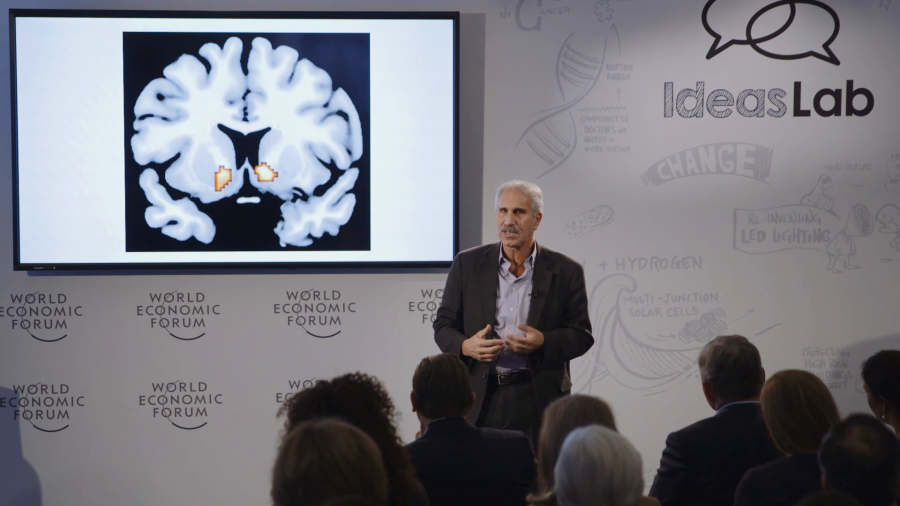
Why do we do the things that we do? Why do we sometimes choose to be loving parents and other times engage in irrational self-destructive behaviors? What drives us to sometimes be altruistic and other times make decisions that really threaten our very survival? Well, the answer lies in our brains. Our brains evolved to ensure that we repeat behaviors that will lead to our survival.