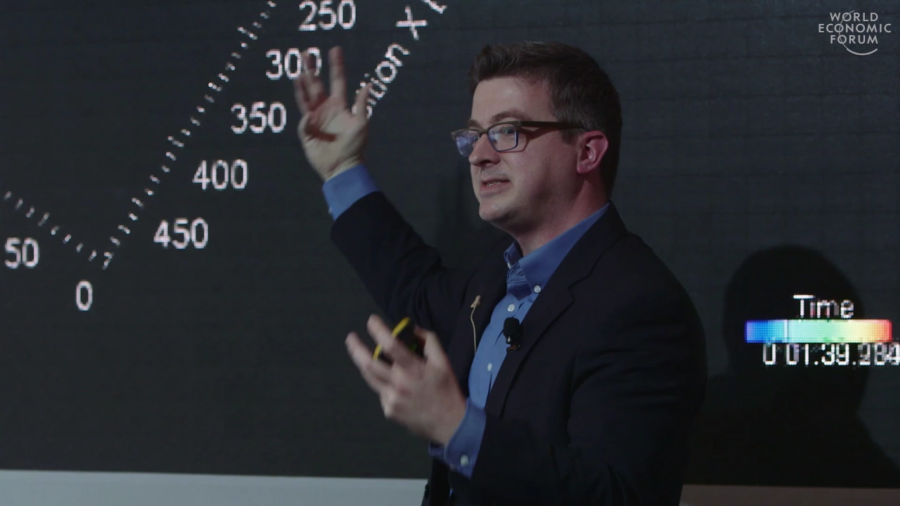
The goal of MICrONS is threefold. One is they asked us to go and measure the activity in a living brain while an animal actually learns to do something, and watch how that activity changes. Two, to take that brain out and map exhaustively the “wiring diagram” of every neuron connecting to every other neuron in that animal’s brain in the particular region. And then third, to use those two pieces of information to build better machine learning. So let it never be said that IARPA is unambitious.
Archive

The thing that makes us unique is our complexity. But not complexity in some generic sense. Nature is rife with complexity. What makes us special is the complexity of our brains.
One of the most important insights that I’ve gotten in working with biologists and ecologists is that today it’s actually not really known on a scientific basis how well different conservation interventions will work. And it’s because we just don’t have a lot of data.
The key molecule of optogenetics is a light-sensitive protein called channelrhodopsin, which is extracted from green algae. Scientists can insert channelrhodopsin into memory cells. Subsequently, scientists can even activate these with blue light which they deliver deep inside the brain with optic fibers.

