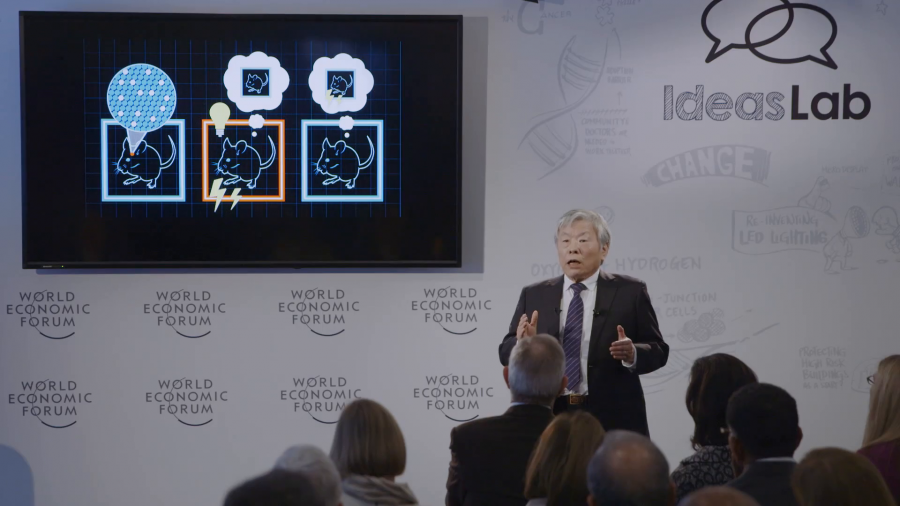
The key molecule of optogenetics is a light-sensitive protein called channelrhodopsin, which is extracted from green algae. Scientists can insert channelrhodopsin into memory cells. Subsequently, scientists can even activate these with blue light which they deliver deep inside the brain with optic fibers.